Configuration & Manifests
All pipelines are linked to an upstream Git repository (Github, Gitlab, Bitbucket, etc.). This repository contains all the required manifests and is regarded as the source of truth for pipelines. This makes pipeline changes easily auditable and comparable, and also keeps the control of manifests in the hands of the user.
Repo Structure
The repository is expected to be as structured as follows:
file1.yml
root_folder/ #Root folder entered when registering pipeline
pipeline.yaml
parameters.yaml
folder/
file2.yml
In this example, file1.yml and root_folder are both at the root level of the repository. GreenOps supports specifying a path to a specific folder in a repo, allowing multiple configurations to be stored in the same repository.
There are two required files that are expected to be there in the folder path specified when creating a pipeline (in this case it is root_folder):
- pipeline.yaml - This holds the actual pipeline manifest, which is in the form of an Argo Workflow.
- params.yaml - Workflows are often reused, for different applications, so this is a separate file where different parameters can be entered for the same boilerplate workflow. GreenOps will automatically inject the parameters into the workflow during runtime.
Both of these files can be edited as YAML if desired, or via the no-code GreenOps UI.
Here is an example of a pipeline.yaml and params.yaml file:
params.yaml:
arguments:
parameters:
- name: application-name
value: testapp-dev
- name: revision
value: main
- name: argocd-server-address
value: 192.168.64.21:3264
pipeline.yaml:
metadata:
generateName: deploy-testapp-
namespace: argo
spec:
entrypoint: starter
templates:
- name: starter
steps:
- - name: deploy-to-dev
templateRef:
name: argocd-step
template: argocd-sync-and-wait
arguments:
parameters:
- name: application-name
value: "{{workflow.parameters.application-name}}"
- name: revision
value: "{{workflow.parameters.revision}}"
- name: argocd-server-address
value: "{{workflow.parameters.argocd-server-address}}"
This pipeline simply syncs an Argo CD application called testapp-dev. The Argo Workflow references a template called argocd-sync-and-wait which carries out this action. GreenOps injects the variables specified in the params.yaml file into the workflow before running it. As this example illustrates, it makes workflows extremely portable and simple to reuse.
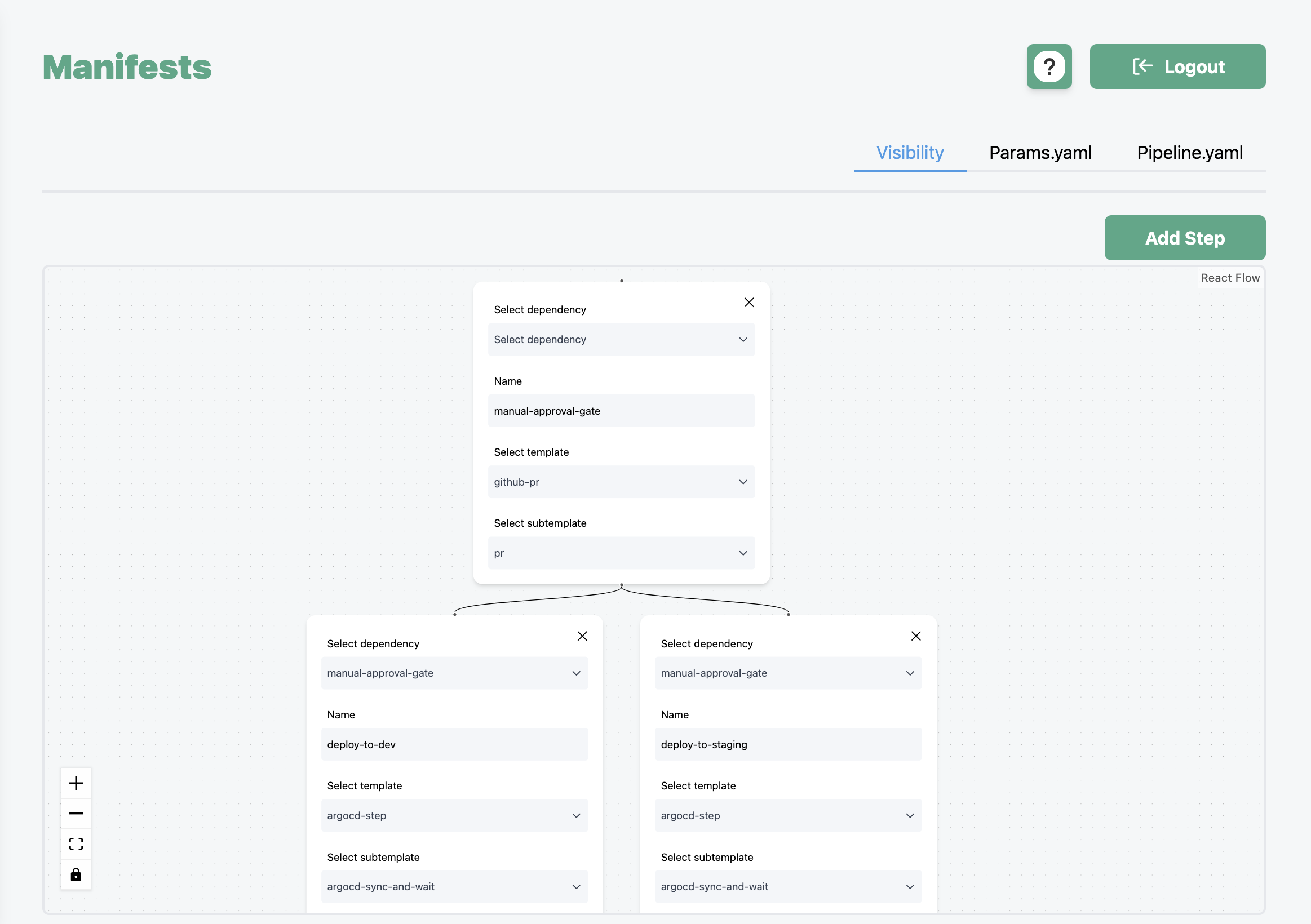
Using the UI
The deployment pipeline manifests can be created/updated by writing YAML directly, or by using the GreenOps UI.
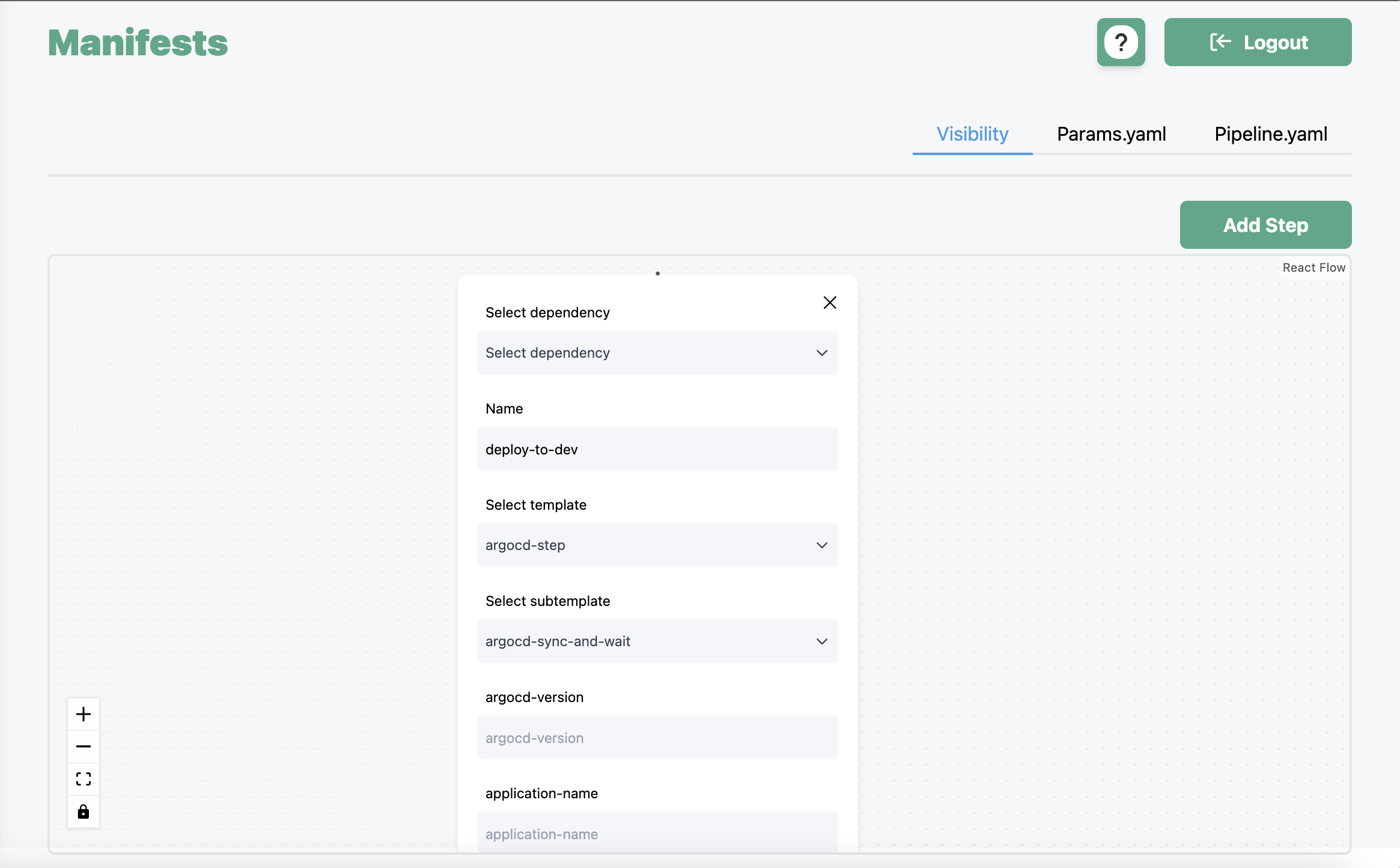
The manifest creator uses templates to get the information for each step.
In this example, the argocd-sync-and-wait template was selected, and the parameters are being filled out for the pipeline. Clicking on the pipeline.yaml and params.yaml tabs in the top right corner would provide the YAML versions of the manifests.
The UI supports any number of pipelines and any number of steps. Complex pipelines with parallel executions, DAGs, and custom steps are supported, as well as simple linear pipelines. An example of a simple DAG is shown below.